Parent page: PCB Panels
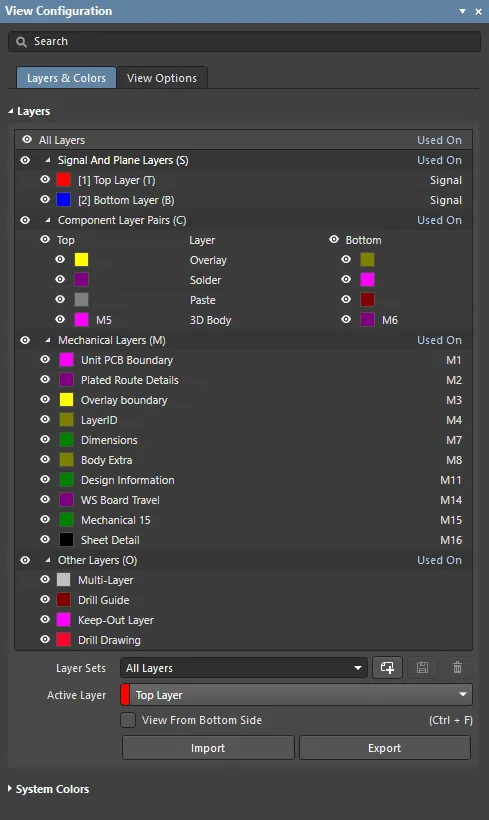
Display related settings are configured in the View Configuration panel.
Summary
The View Configuration panel is used to configure what is currently displayed in the workspace and how it is displayed. This includes layer visibility and color, object visibility and transparency, masking and dimming levels, the current single layer mode, and a number of additional workspace display features, such as the display of net names on pads, via and tracks.
The panel is also used to add mechanical layers to the design, an unlimited number of mechanical layers can be added. Mechanical layers can also be paired in the View Configuration panel to function as special-purpose Component Layers, for roles such as component courtyards or glue dots.
Panel Access
The panel is accessed from the PCB editor in the following ways:
- Click View » Panels » View Configuration.
- Click the
 button at the bottom-right of the workspace then select the View Configuration option.
button at the bottom-right of the workspace then select the View Configuration option.
- Click the color swatch
 on the Layer Sets control at the bottom left of the workspace.
on the Layer Sets control at the bottom left of the workspace.
- Press the L shortcut key to open the panel with the Layers & Colors tab displayed.
- Press the Ctrl+D shortcut keys to open the panel with the View Options tab displayed.
Content and Use
The panel content is divided into two tabs. Click on a tab at the top of the panel to display the options available on that tab:
- Layers and Colors tab - includes options to control the visibility of available layers, and add, rename or delete mechanical layers.
- View Options tab - includes options to select, save or load the Configuration of layer colors/visibility, configure the visibility of object-types, control the masking and dimming levels, and configure other display related options.
Within each tab, the content is arranged in collapsible sections that are opened and closed using the arrow icon associated with each section heading. The information included is arranged by matching sections and each collapsible section is opened/closed in the same manner. The options that are available will depend on the current Layout Mode.
Setting the Color
Each layer includes a small color button; click to display the color selector as shown below.

The panel includes:
- A grid of 10 x 8 predefined color buttons. Click a button to select that color.
- A Custom Color row of up to ten custom colors.
Custom colors can be defined by performing the following:
- Click Define Custom Colors to expand the color palette to also display the Custom Color Palette.
- Use the horizontal slider in the center of the Custom Color Palette to select a base color then click anywhere on the palette to brighten or darken that color.
- Alternatively, enter the Hex or RGB values into the appropriate fields in the Custom Color Palette.
- Click the Apply button to add the new color to the Custom Color row and apply that color to the layer being edited.
Displaying or Hiding a Layer
Each layer or system attribute (such as selections or DRC errors), can be displayed or hidden. Click the visibility icon ( ) to toggle the visibility off and on.
) to toggle the visibility off and on.

Where appropriate, each group also includes a visibility icon ( ). For example, in the image above:
). For example, in the image above:
- To the left of the string Component Layers (C) there is a visibility icon; click this to toggle the visibility of all component layers on/off.
- To the left of the string Top there is a visibility icon; click this to show/hide all top side component layers. The Bottom side layers can also be displayed/hidden in the same way.
Controlling Visibility from the Keyboard
In a busy PCB design, layers are often toggled on and off during the design process. To help with this, layer visibility can be changed using keystrokes in the following way:
- Press the L shortcut to display/make the Layers & Colors tab of the View Configuration panel active. The panel's title bar will become colored indicating that it is the active element in the software.
- Press the appropriate Shortcut key on the keyboard to access a layer or set of layers; the shortcut key is displayed in parentheses next to each layer or layer set. For example, the C shortcut in the image above accesses the Component Layer set of layers.
- If you have accessed a set of layers, press Spacebar to toggle the visibility of all layers in that set.
- If you have accessed a layer, its visibility will toggle immediately and the Spacebar can then be used to toggle it again.
- Press the Up or Down arrow keys to move up or down through the list, for example, to access a specific mechanical layer or a pair of component layers. You can then use the Spacebar to toggle the visibility of that layer/layer pair.
Permanently Display a Layer in the Single Layer Mode Display
To include a layer in the Single Layer Mode display, perform a Ctrl+Click on the eye icon associated with the desired layer to add that layer into Single Layer Mode display; a square will appear behind the eye icon ( ) to denote that layer wil be permanently displayed in Single Layer Mode.
) to denote that layer wil be permanently displayed in Single Layer Mode.
Layers & Colors Tab
Layers

- Signal and Plane Layers – click the color button to change that layer's color, as described previously in the Displaying or Hiding a Layer section. Click the visibility icon (
 ) to toggle the display of an individual signal or plane layer. Signal and Plane layers are added, named and removed in the Pad-Via Layer Editor.
) to toggle the display of an individual signal or plane layer. Signal and Plane layers are added, named and removed in the Pad-Via Layer Editor.
- Component Layer Pairs – these layers are paired so that when a component is flipped from the top side to the bottom side of the board (L shortcut as a component is being moved), the software can flip the top side layer contents onto their paired bottom side layers. User-defined component layer pairs can be defined using Mechanical layers.
- Mechanical Layers – these are general purpose drawing layers. These layers can also be paired and when paired, they become a Component Layer Pair. Component Layer Pairs are used for special-purpose roles, for example glue dots, or 3D component bodies. To rename a mechanical layer, right-click on it to open the Edit Layer dialog from the context menu.
- Other Layers – these are system managed layers, for example, objects placed on the multi-layer automatically appear on all signal layers, and objects placed on the keepout layer act as a keep-clear boundary on all signal layers.
- Layers Sets - use the drop-down to select an existing Layer Set. The following buttons are used to create, save, and delete Layer Sets:
-
 - click to create a new Layer Set. The set will appear as My Layers in the drop-down. Each subsequent Layer Set added will be numbered.
- click to create a new Layer Set. The set will appear as My Layers in the drop-down. Each subsequent Layer Set added will be numbered.
-
 - click to save when you create a new Layer Set or if you have edited the currently selected Layer Set. The creating and renaming of a Layer Set do not require a save action, as those functions save automatically. Changing the configuration of enabled layers, including your own Layer Set, does require a save action.
- click to save when you create a new Layer Set or if you have edited the currently selected Layer Set. The creating and renaming of a Layer Set do not require a save action, as those functions save automatically. Changing the configuration of enabled layers, including your own Layer Set, does require a save action.
-
 - click to delete the currently selected Layer Set.
- click to delete the currently selected Layer Set.
- Active Layers - use the drop-down to view one of the various Active Layers on the PCB individually.
- View From Bottom Side - check this box to view the Layer Sets from the bottom side.
- Import - click this to import the desired PCB Layer Set File (*.layerset).
- Export - click this to export the desired Layer Set as a PCB Layer Set File (*.layerset).
Refer to
The Board page to learn more about the layers in a printed circuit board.
Refer to the
Defining the Layer Stack page to learn how to configure the layer stack.
To configure and edit a pair of mechanical layers as a Component Layer Pair:
1. Right-click anywhere in the Layers region of the Layers & Colors tab, then select Layer Stack Manager to open the Layer Stack Manager. Here, you can assign a name or comment to a Layer, add Stack Symmetry and Library Compliance for a board, and view the number of Layers, Dielectrics, Conductive Thickness, Dielectric Thickness, and Total Thickness of the board.
2. Right-click anywhere in the Layers region of the Layers & Colors tab, then select Add Component Layer Pair from the context menu. A new mechanical layer will be automatically added to bottom of the Component Layer Pairs (C) section.
3. Right-click anywhere in the Layers region of the Layers & Colors tab, then select Add Mechanical Layer from the context menu. A new mechanical layer will be automatically added to the Mechanical Layers (M) section.
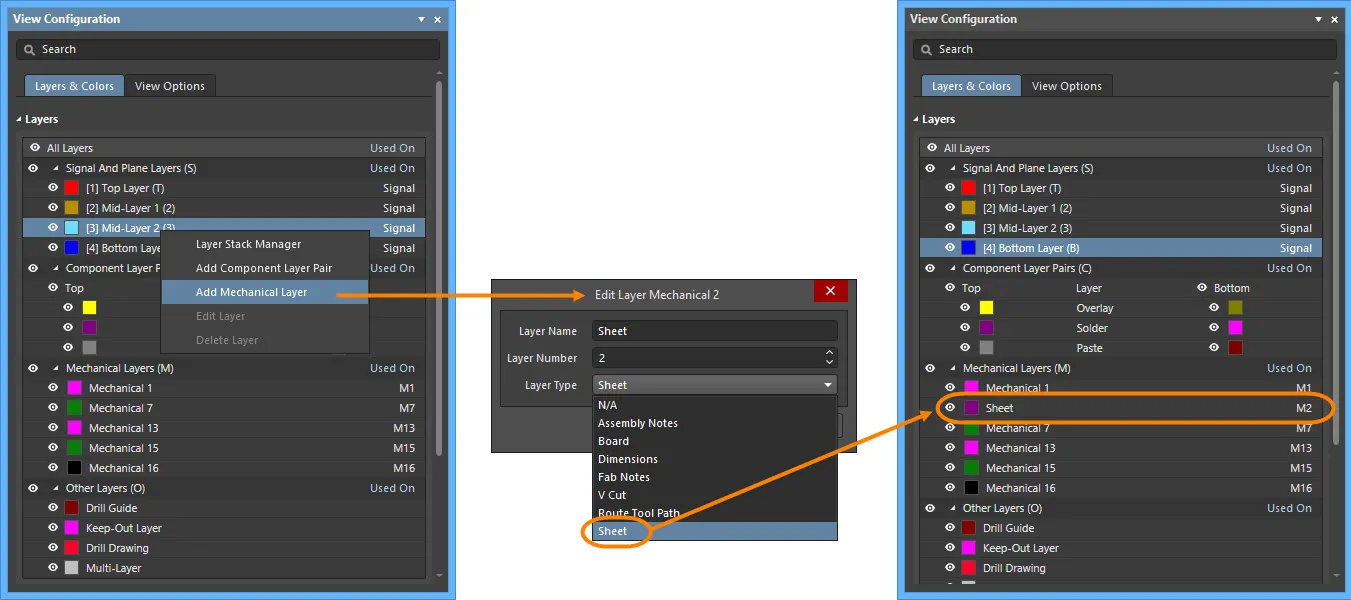
4. Right-click or double-click on a Mechanical Layer to open the Edit Layer dialog. A Mechanical Layer may reside in the Component Layer Pairs (C) or Mechanical Layers (M) section. When a Mechanical Layer is renamed, the Edit Layer dialog's name will also reflect the name of the Mechanical Layer. For instance, if "Mechanical Layer 15" is being edited, the Edit Layer dialog will displayed as "Edit Layer Mechanical Layer 15" when windowed. When accessing the Edit Layer dialog, you may edit:
- Layer Name - use this text box to rename the Mechanical Layer.
- Layer Number - use this text box to manually input the desired Layer Number. If the number is unavailable, an exclamation point (
 ) will appear, and an available Layer Number will need to be selected to continue.
) will appear, and an available Layer Number will need to be selected to continue.
- Layer Type - use this drop-down to select the Layer Type in which you'd like the Mechanical Layer to reside. The chosen Layer Type will then appear in parenthesis alongside the name of the Mechanical Layer.
Any number of Mechanical Layers can be added to the PCB. Mechanical Layers also support defining the Layer Number, and setting the Layer Type. There are two sets of Layer Type options, a set for individual mechanical layers, and a set for Layer Pairs, as shown below.


As with other component layers, the software will automatically pre-pend the word Top or Bottom to the name to distinguish to which layer the pair is being referred.
To delete a layer, you can right-click on the desired layer and select Delete Layer. Depending on how the layer is being utilized, you will come across three options:
- If the layer can not be deleted because it contains component primitives that cannot be removed, an error pop-up will appear to alert you that the action cannot be completed.

- If the layer is associated with primitives that can be removed, a pop-up will appear to ask for confirmation of deletion.

3. If the layer is not associated with primitives, it will be deleted immediately upon clicking Delete Layer, without confirmation.
Only unused mechanical layers can be paired.
System Colors
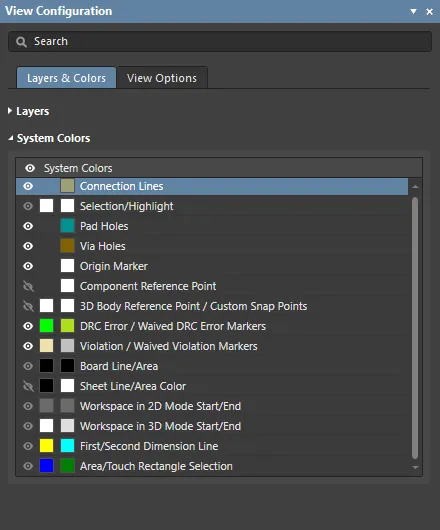
- System Colors – use these controls to configure the color and visibility of special system display features, such as pad holes, the origin marker and DRC errors.
View Options Tab
General Settings
 The General Settings change between 2D and 3D modes; hover the mouse to show the differences.
The General Settings change between 2D and 3D modes; hover the mouse to show the differences.
- Configuration – a configuration is a pre-packed definition of layer color and layer visibility settings. Select an existing configuration from the drop-down or use the buttons to create, save or delete a configuration. Custom configurations save both of the current / last used 2D and 3D display settings.
-
 - click to create a new Custom Configuration then type in a new name and click the
- click to create a new Custom Configuration then type in a new name and click the  button.
button.
-
 - click to save when you create a new Custom Configuration or if have edited the currently selected Custom Configuration.
- click to save when you create a new Custom Configuration or if have edited the currently selected Custom Configuration.
-
 - click to delete the currently selected Custom Configuration.
- click to delete the currently selected Custom Configuration.
Custom Configurations that have been created and saved are automatically loaded and available for selection from the Configuration field's drop-down listing.
- 3D - use the buttons to switch between the 2D layout mode and the 3D layout mode. Alternatively, press the 2 or 3 shortcut keys or use the commands in the View menu. Additional options will appear in 3D mode and are described below.
- Single Layer Mode – the workspace display can be cycled through the Single Layer Modes at any time by pressing the Shift+S shortcut. This will leave the active or current layer shown in its normal display color and intensity, with all other visible layers grayed out or hidden depending to which Single Layer mode you switch. There are three Single Layer display modes available:
- Gray - display all other layers in different shades of gray, the shade is based on the layer's current color.
- Mono - display all other layers in the same shade of gray.
- Hide - hide all other layers.
If you are in Single Layer Mode, the current mode is displayed next to the Off/On buttons. In the image above, the current mode is Hide. This text is also a link to quickly access the settings where you can configure the available Single Layer Modes in the PCB Editor - Board Insight Display page of the Preferences dialog.
Use the Masked Objects slider in the Mask and Dim Settings region of the View Options tab of the panel to control the brightness of other layers in the Gray or the Mono Single Layer modes.
- Show Grid (2D mode only) - the software has two display grids, referred to as the Fine and Coarse grids. The Fine grid is the current snap grid (as shown on the Status bar); the Coarse grid can be set to be equal or any whole number multiple of this grid.
- Show Grid checkbox - the checkbox gives a quick way to toggle the visibility of both the Fine and Coarse grids on and off.
- Show Grid color selector - allows the color of both grids to be changed. The color you choose is applied to the Fine grid, with the Coarse grid being automatically set to a lighter shade of the same color.
The current Snap grid and the configuration of the Display grids is managed in the Grid Editor dialog. Press Ctrl+G to open the dialog or press G to display a quick-select menu of grid settings.
Refer to the PCB Grids System page to learn more about grids.
- Projection (3D mode only) - determines the projection of the 3D view. Choose from:
- Orthographic - choose this option to see the exact position of objects and text on the PCB without being obscured by surrounding objects.
- Perspective - choose this option for a more realistic 3D view of the PCB.
- Show 3D Bodies (3D mode only) - controls the display of 3D Bodies. Use the Shift + Z shortcut to toggle this option on/off at any time when working in 3D mode. It also is possible to control the display of each model kind (extruded or generic) using an advanced setting. To do this, click the Advanced button on the System - General page of the Preferences dialog. In the Advanced Settings dialog, the Legacy.PCB.3DModelsShowMode preference controls the display of model types, supporting the Value - 0 (both), 1 (Generic only), 2 (Extruded only).
Object Visibility (2D only)

- Object Visibility - as well as controlling the display of objects in the workspace by toggling layers on and off, another approach is to control the visibility and transparency of objects based on their object-type.
- Visibility - control the visibility of specific object-types by clicking the appropriate visibility icon. Click the All Objects visibility icon to toggle the visibility of all objects then enable the visibility of specific object-types.
- Name - lists all objects that may be adjusted visually.
- Draft - enable to display that object type as an outline.
- Transparency - adjust the transparency to make that object type see through. Setting an object to transparent means you can see when one object covers another object, for example, where the end of a track segment meets a pad.
Easily restore your preferred visibility settings by creating a Custom Configuration in the General Settings region of this panel.
3D Settings (3D only)

Available only in 3D mode, these options are used to control the presentation of the board in 3D Layout Mode.
- Board thickness (Scale) - controls the vertical scale of the 3D view to make it easier to differentiate the layers, for example, when reviewing the layer-to-layer connections of an internal blind via. Drag the slider to set the vertical scaling between 1 and 100 times the actual board thickness.
- Colors - the default presentation is to render the 3D board using Realistic colors based on the Configuration currently selected in the General Settings section of this panel. Click the By Layer button to display the 3D view using the current 2D layer color assignments.
- Layer - click a color swatch to display the color selector. Refer to the Setting the Color section to learn more about using the selector.
- Transparency - use the sliders to control the transparency of each layer.
Mask and Dim Settings

To help manage the display of the large number of objects that can exist even in a simple PCB design, the PCB editor has the ability to fade objects that are not of interest. For example, if you click on a net in the Nets mode of the PCB panel and the panel drop-down is set to Dim or Mask, then all objects that do not belong to that net are faded. This allows you to more easily focus your attention on a specific design element, such as a net or a class of nets, class of components, objects targeted by a certain design rule, and so on.
- Dimmed Objects – objects that are currently dimmed retain their color but are faded. Use this slider to configure how much dimmed objects are faded. Dimmed objects can be edited.
- Highlighted Objects - when you have Dim enabled and click on an object in a panel, for example, a net in the Nets mode of the PCB panel, that net is also highlighted as all other nets are dimmed. Highlighted objects have their color whitened to make them stand out. This slider is used to control the amount of white added to the highlighted objects.
- Masked Objects - objects that are currently masked are displayed in gray and cannot be edited. Use this slider to configure how much masked objects are faded.
Masking and Dimming can be enabled in various locations, such as the PCB panel, the PCB Filter panel and the PCB Rules and Violations panel.
Press the Shift+C shortcut to clear any applied masking or dimming.
Additional Options (2D only)
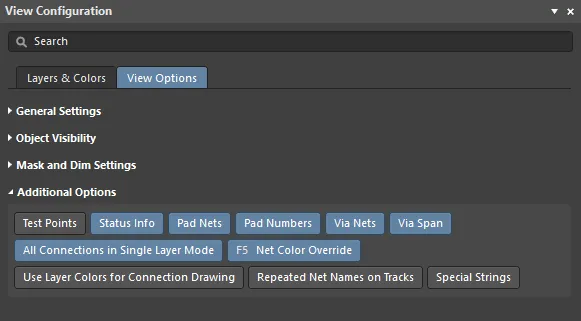
- Test Points - enable this option to display additional information on pads and vias that have been configured as testpoints. A Pad or a Via can be configured as a testpoint by enabling the Fabrication and/or Assembly Testpoint options in the relevant mode of the Properties panel. Testpoints are indicated by the addition of the string
<Layer> Fab Testpoint or <Layer> Assy Testpoint to the pad/via.
- Status Info - enable this option to have summary information, such as coordinate position and layer, displayed in the Status Bar when hovering over an object in the design workspace.
- Pad Nets - enable this option to display the associated net name on a pad. Note that net names will only become visible if you are zoomed in close enough.
- Pad Numbers - enable this option to display pad numbers. Note that pad numbers will only become visible if you are zoomed in close enough.
- Via Nets - enable this option to display the relevant net name on a via. Note that net names will only become visible if you are zoomed in close enough.
- Via Span - enable this option to display the length in which the via is allowed to span. The properties of placed vias (diameter, hole size, etc) are then defined either by design rules, or manually. Note that net names will only become visible if you are zoomed in close enough. The layer numbers in the via span can be displayed inside all via types.
- All Connections in Single Layer Mode - enable this option to always display all of the connection lines when in Single Layer Mode. With this option disabled, all connection lines that do not start or end on the current layer are also hidden when switching to Single Layer Mode as it is assumed that they are not relevant.
- Net Color Override - each net can be assigned a color. To configure the color, double-click on that net's name in the Nets mode of the PCB panel; the Edit Net dialog will open. The color is automatically applied to that net's connection lines and also can be applied to the routing by enabling this option. Color is applied to the routing in accordance with the current settings in the PCB Editor - Board Insight Color Overrides page of the Preferences dialog, where you choose a Pattern option to define how the color is applied and choose a Zoom Behavior to define when the color is applied. Press the F5 shortcut to toggle the Net Color Override option on and off.
- Use Layer Colors for Connection Drawing - enable this option to display the connection lines using the colors of the start and end layers that the connection line travels between. The connection lines are displayed in pure layer color at the object they start/end at, morphing between those layer colors along the length of the connection line. This feature is helpful when you are routing a multi-layer board as it indicates the target layer that the connection being routed, must go to. Note that color morphing is only applied to connections that travel from one layer to another, if the connection starts and ends on the same layer it retains the assigned net color.
- Repeated Net Names on Tracks - enable to show repeated net names on tracks.
- Special Strings - when the option is enabled, any placed Strings that are formed from converted Special Strings will be superimposed (labeled) with the unconverted Special String name. Zoom in on a String to see its label overlay.
