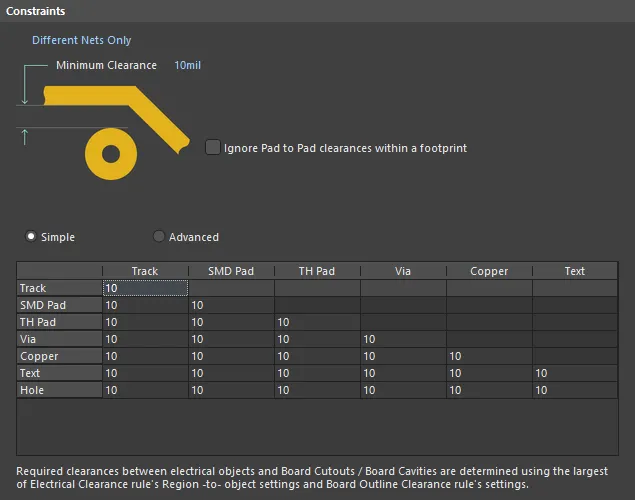
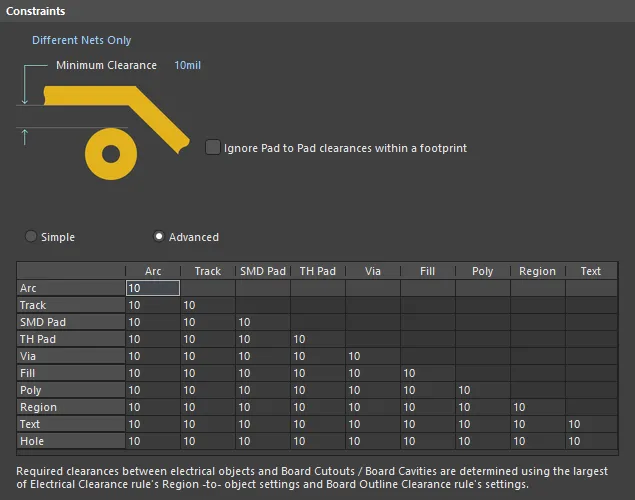
Electrical Rule Types
The design rules of the Electrical category are described below.

The Electrical category of design rules.
Clearance
Default Rule: required
This rule defines the minimum clearance allowed between any two primitive objects on a copper layer. Either a single value for clearance can be specified, or different clearances for different object pairings, through use of a dedicated Minimum Clearance Matrix. The latter, in combination with rule-scoping, provides the flexibility to build a concise and targeted set of clearance rules to meet even the most stringent of clearance needs.
Constraints
The rule scope returns a set of objects, the constraints detailed below are then applied to that set of objects:
-
Connective Checking - the set of net objects returned by the rule scope can then be further narrowed down in the following ways:
-
Different Nets Only- constraint is applied between any two primitive objects belonging to different nets (e.g., two tracks on two different nets). -
Same Net Only- constraint is applied between any two primitive objects belonging to the same net (e.g., between a via and pad on the same net, or two track segments in the same net). -
Any Net- constraint is applied between any two primitive objects belonging to any net in the design. This is the most comprehensive of the three options and covers the possibility of the objects belonging to the same net, or different nets. - Different Differential Pair - constraint is applied between any two primitive objects belonging to different nets of different differential pairs (e.g., a track in DiffPair1 and a track in DiffPair2). The rule does not apply between primitives in the two nets in the same differential pair (e.g., DiffPair1_P and DiffPair1_N). Use this constraint to configure the clearance between the differential pairs.
-
Same Differential Pair - constraint is applied between any two primitive objects belonging to the different nets in the same differential pair (e.g., a track in TX_P and a track in TX_N). Use this constraint to configure the clearance when the nets in the differential pair must be closer together than allowed by the general clearance.
Learn more about Differential Pair Clearance Checking
-
- Ignore Pad to Pad Clearances within a footprint - toggle this option on/off to specify whether clearances between pads in the same component footprint are ignored. This option is disabled by default.
- Minimum Clearance - the value for the minimum clearance required. A value entered here will be replicated across all cells in the Minimum Clearance Matrix. Conversely, when a different clearance value is entered for one or more object pairings in the matrix, the Minimum Clearance constraint will change to N/A, to reflect that a single clearance value is not being applied across the board.
- Minimum Clearance Matrix - provides the ability to fine-tune clearances between the various object-to-object clearance combinations in the design.
Working with the Clearance Matrix
For many users, there is no great difference between Track and Arc primitives. And when it comes to Fill, Region, and Polygon objects, most users just see these as more 'copper.' With this in mind, the minimum clearance matrix for the Clearance rule has been enhanced to operate in two modes:
- Simple - in this mode, Track and Arc objects (including Track Keepout and Arc Keepout objects) are combined into the single Track entry. Fill, Poly, and Region objects (including Fill Keepout and Region Keepout objects) are combined into the single Copper entry. The Simple mode is the default mode, regardless of whether opening an existing design or a new design.
- Advanced - this mode is the traditional matrix, with all objects presented.
Definition of clearance values in the matrix can be performed in the following ways:
- Single-cell editing - to change the minimum clearance for a specific object pairing. Click on a cell to select it for editing.
-
Multi-cell editing - to change the minimum clearance for multiple object pairings:
- Use Ctrl+Click, Shift+Click, and Click+Drag to select multiple cells in a column.
- Use Shift+Click, and Click+Drag to select multiple contiguous cells in a row.
- Use Click+Drag to select multiple contiguous cells across multiple rows and columns.
- Click on a row header to quickly select all cells in that row.
- Click on a column header to quickly select all cells in that column.
With the required selection made (either a single cell or multiple cells), making a change to the current value is simply a case of typing the new value required. To submit the newly entered value, either click away on another cell, or press Enter. All cells in the selection will be updated with the new value.
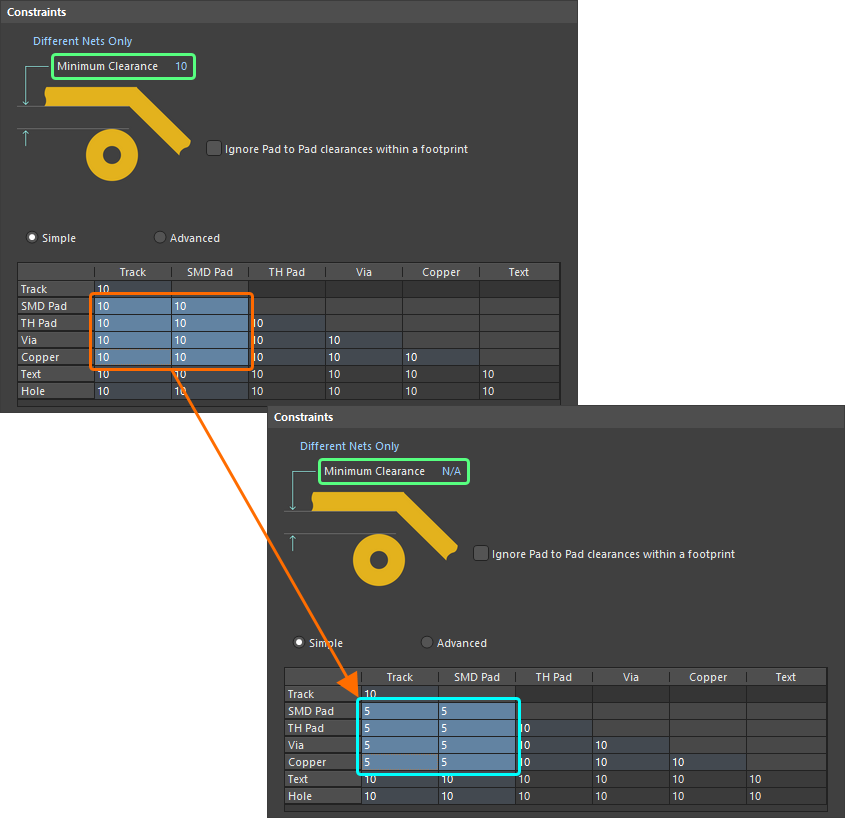
Example multi-cell editing. Notice that as different values for clearance now exist for one or more object pairings, the Minimum Clearance constraint has changed to N/A, to reflect that a single clearance value is no longer being applied for all object-to-object clearance combinations.
Hole-to-Object Clearance Checking
Designers can check clearances between the edges of drill holes and neighboring copper objects on signal layers. This is particularly beneficial in preventing the routing of track too near to a drilled hole, which could otherwise suffer from any potential wandering of the drill during board fabrication. The row at the bottom of the Clearance rule's minimum clearance matrix is used to define the desired clearances.
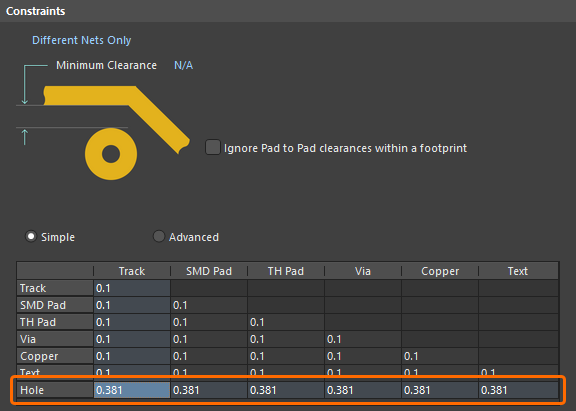
Set clearance values to catch any copper objects that are too close to the edges of drill holes in the design.
Split Plane Clearance Checking
Designers can also check clearances between split plane regions on internal plane layers. How clearance is defined depends on the mode in which you are using the minimum clearance matrix:
- Simple mode - specify the required split plane-to-split plane clearance value using the Copper-Copper cell.
- Advanced mode - specify the required split plane-to-split plane clearance value using the Region-Region cell.
A violation will appear in the form:
Clearance Constraint: (<CurrentClearance> < <DefinedClearance>) Between Split Plane (<NetName>) on <InternalPlaneLayerName> And Split Plane (<NetName>) on <InternalPlaneLayerName>,
for example:
Clearance Constraint: (32.36mil < 34mil) Between Split Plane (GND) on Internal Plane 1 And Split Plane (NetC6) on Internal Plane 1
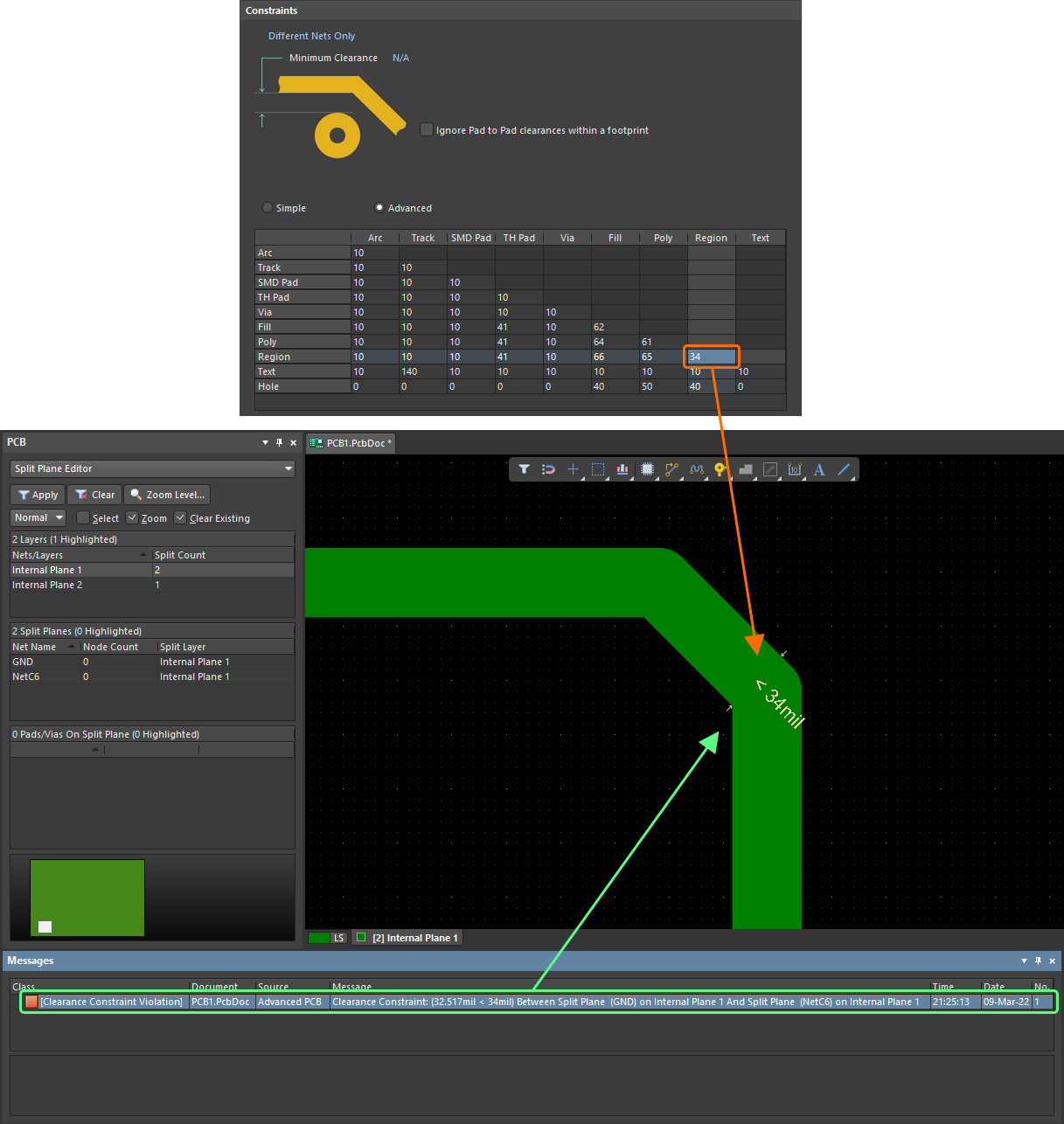
Clearance checking between split plane regions on an internal layer. In this case, the clearance value of 34mil has been entered in the Region-Region cell, as clearances are being defined using the Advanced mode of the matrix.
Differential Pair Clearance Checking
Differential pairs present unique design challenges, often requiring a specific within-pair clearance as well as a pair-to-pair clearance, and potentially a third rule to control the pair-to-all other nets, clearance. To support this, the Constraints region includes the dropdown where you can choose Same Differential Pair and Different Differential Pair options.
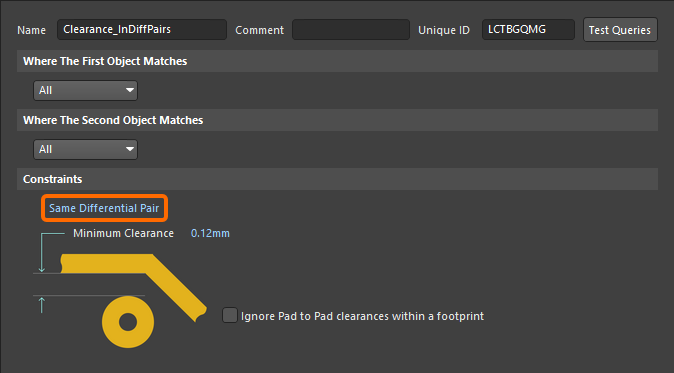
For example, if the nets within the differential pairs require a tighter clearance than the general board clearance, this can be achieved by using the Same Differential Pair constraint option, as shown below. Note that even though the rule scope applies to All net objects in the design, the Constraint setting restricts it to only apply to objects in the Same Differential Pair.
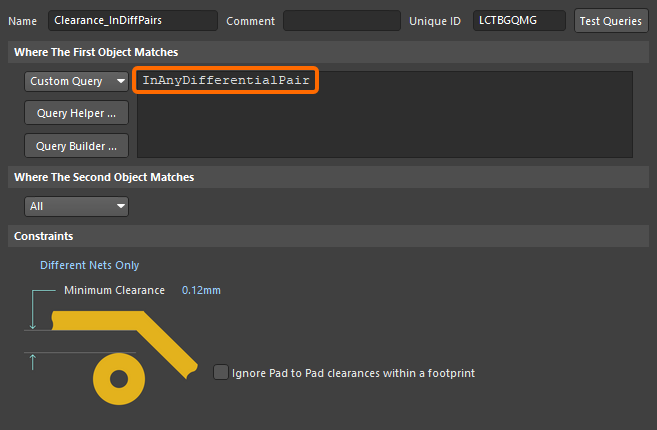
This result could also be achieved by scoping the rule to only apply to differential pair objects (e.g., InAnyDifferentialPair), as shown below. Note that this rule would also apply between a net in a differential pair to any other net object in the design, so this approach should only be used if you have other higher priority rule(s) that define the DiffPairNet-to-DiffPairNet and/or DiffPairNet-to-Any requirements. If this approach is used, the Priority of the differential pair rules must also be configured correctly, with the rule with a tighter clearance requirement having a higher priority.
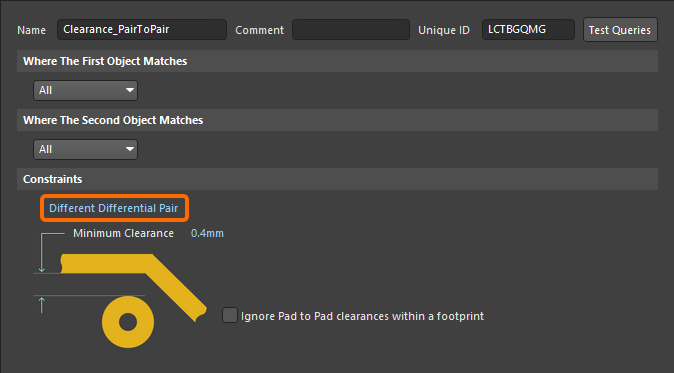
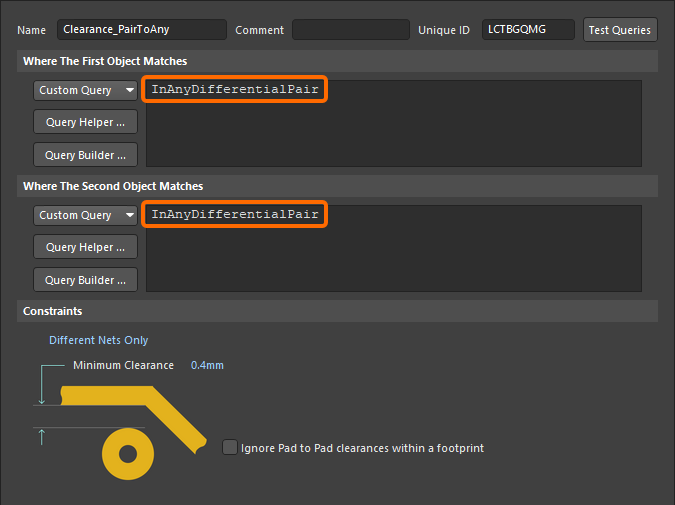
A similar approach can be used to control the clearance between differential pairs. The image below shows how the Different Differential Pair constraint can be used to achieve this.
As with the previous example, it could also be achieved using the rule scope, instead of the Different Differential Pairs constraint. Remember that the rule priorities must be configured so the rule with the tighter clearance requirement has a higher priority.
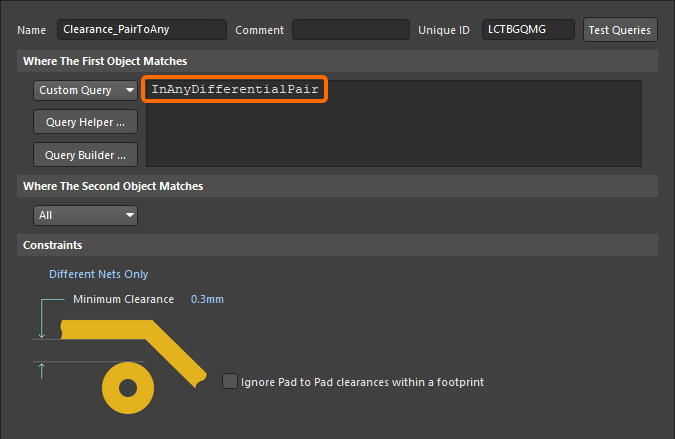
To define a different clearance from a differential pair net to any other net object, the following rule could be used.
This could be further refined so that it only applies between differential pair objects and non-differential pair objects, as shown below.
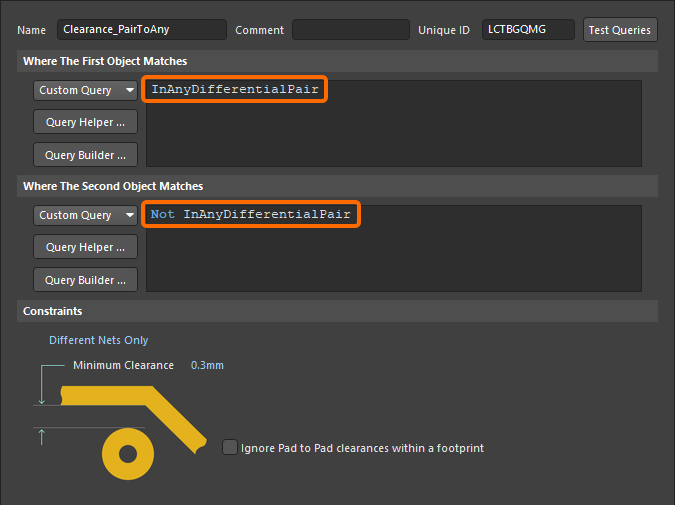
Learn more about Differential Pair Routing. Learn more about scoping Differential Pair design rules.
Rule Application
Online DRC, Batch DRC, interactive routing #, autorouting #, and polygon placement.
Notes
- # While the DRC can test the clearance of any object kind to any object kind using any sort of rule scoping, the routing engines do not support this level of granularity. For example, the base clearance rule might require all tracks to have a clearance of 1 mm, with a higher priority rule requiring tracks greater than 10 mm in length to have a clearance of 2 mm. In this situation, the interactive routing engine will obey the base clearance rule, ignoring the higher priority, greater than 10 mm in length, rule. Another example is routing with arcs in corners. If the clearance rule specifies a higher clearance for arcs than for tracks, and you are interactively routing with arcs in the corners, the interactive routing engine will ignore the arc setting and obey the track setting, placing the corner arcs to have the same clearance as the track segments. In both of these examples, as soon as routing is completed, the Online DRC will flag those situations as violations.
-
When defining the constraints for the rule, the Connective Checking option would typically be set to
Different Nets Only. An example of whenSame Net OnlyorAny Netcould be used is to test for vias being placed too close to pads or other vias on the same net, or any other net. - The minimum clearance matrix applies irrespective of the connective checking method specified. If different clearances are required between objects on the same net, to those defined for objects on different nets, be sure to define separate clearance rules as required to suit.
- The applicable use of the clearance matrix depends on the rule scoping. For example, with scoping of ALL-ALL, all cells in the matrix are applicable (i.e. all possible object pairings). However, if scoping were set to IsVia-IsTrack, then only the single cell for the Via-Track object pairing would be applicable, and all other cells in the matrix left unused.
-
When defining a clearance rule for a polygon, it is the primitives of the polygon that the rule is actually applied to, rather than the polygon itself. The keyword entry
InPolygon(orInPoly) should be included in the Full Query in this case, instead ofIsPolygon(orIsPoly). The specific polygon clearance rule must also be given a higher priority than any general clearance rule, if it is to have any effect. - During routing (and similar operations), the rules engine constantly checks for obstacles around the point of editing. The area scanned will include the area of the primitive plus the clearance area required around that primitive. That means the larger the clearance defined in the rules the larger the area that needs to be scanned, and therefore, the slower that the operation will be. If a large clearance is only needed for a small number of objects, you can avoid slowing the routing engine by adding a keepout around these specific objects, instead of defining a large clearance rule for them.
- When using the Dielectric Shapes Generator (in Printed Electronics) in Auto mode, the dielectric shape is automatically expanded to satisfy the requirement of the applicable Clearance Constraint design rule.
- In Printed Electronics, net-to-net clearances are tested on all layers, not just the same layer.
Short-Circuit
Default Rule: required
This rule tests for short circuits between primitive objects on the copper (signal and plane) layers. A short circuit exists when two objects that have different net names touch.
Constraints

Default constraints for the Short-Circuit rule
Allow Short Circuit - defines whether the target nets falling under the two scopes (full queries) of the rule can be short-circuited or not. If you require two different nets to be shorted together, for example when connecting two ground systems within a design, ensure that this option is enabled.
Rule Application
Online DRC, Batch DRC, and during autorouting.
Notes
-
In a Printed Electronics design when different nets cross over on different layers, they are flagged as a short circuit. These cross-overs are isolated by placing a dielectric patch on a non-conductive layer.
-
This rule also applies to Wire Bonding. A violation occurs when a bond wire is connected to a die pad or copper of a different net or when endpoints of bond wires of different nets are connected.
Un-Routed Net
Default Rule: required
This rule tests the completion status of each net that falls under the scope (full query) of the rule. If a net is incomplete then each completed section (sub-net) is listed along with the routing completion. The routing completion is defined as:
(connections complete / total number of connections) x 100
The PCB Editor's Design Rule Checking system typically sees a net as being routed if all nodes in that net (component pads) are connected through the use of net-aware design objects (tracks, arcs, pads, vias, and polygons). These objects are considered connected if they touch each other. However, while simply touching makes a perceived connection to the software, when it comes time to fabricate the board, the fragility of some of these 'connections' can cause critical issues, especially where the objects - for example two contiguous track segments, or a track entering a pad/via - are only slightly touching. Such connections are often referred to as 'Bad Connections', 'Poor Connections', or 'Incomplete Connections'. This rule can also be configured to test for such poor connections.
Constraints
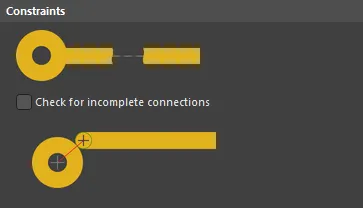
Default constraints for the Un-Routed Net rule
Check for incomplete connections - with this option enabled, the following additional checks on connectivity between applicable design objects are made:
- Track/Arc to Track/Arc - checking that the centerlines, or centers of the ends of the connecting track/arc segments, coincide.
- Track/Arc to Via - checking that the centerline, or center of the end of a track/arc segment, is placed on the shape of the via.
- Track/Arc to Pad - checking that the centerline, or center of the end of the track/arc segment, is placed on the shape of the pad.
- Via to Pad - checking that the center of the via is placed on the shape of the pad.
- Via to Via - checking that the center of one via is placed on the shape of another via.
- Polygon to Track/Arc - checking that the centerline, or center of the end of a track/arc segment, is overlapped by the polygon.
- Polygon to Pad/Via - checking that the center of the Pad/Via is overlapped by the polygon when the Pad/Via uses a direct connection to the polygon.
Rule Application
Batch DRC.
Notes
-
A poor connection will be flagged in the design space using the detailed violation marker,
 , with a corresponding message appearing in the Messages panel.
, with a corresponding message appearing in the Messages panel.
-
Where applicable, a connection line will be drawn between unconnected objects in the net, with data regarding the un-routed net length reflected in the PCB panel (in Nets mode).
-
Some DRC checks require the Un-Routed Net rule to be Batch-enabled for them to work.
-
In Printed Electronics, layer transitions do not require a via, the net analyzer will recognize that the net is not broken if a via is removed from a routed net. A board is defined as Printed Electronics when the Printed Electronics option is enabled in the Layer Stack Manager. Learn more about Printed Electronics.
-
This rule also applies to Wire Bonding. A violation occurs when there is no connection between die pads, bond wires and/or copper objects of the same net.
Un-Connected Pin
Default Rule: not required
This rule detects pins that have no net assigned and no connecting tracks.
Constraints
None
Rule Application
Online DRC and Batch DRC.
Modified Polygon
Default Rule: required
This rule detects polygons that are still shelved and/or have been modified but have not yet been repoured.
Constraints
Default constraints for the Modified Polygon rule
- Allow shelved - if enabled, all polygons that fall within the scope of this design rule, and that are currently shelved, will not be flagged as a violation.
- Allow modified - if enabled, all polygons that fall within the scope of this design rule, and that are currently modified but have not been repoured, will not be flagged as a violation.
Rule Application
Online DRC and Batch DRC.
Creepage Distance
Default Rule: not required
This rule tests the creepage distance between the targeted signals across the board surface through unplated holes, cutouts, and around the board edge.
Constraints
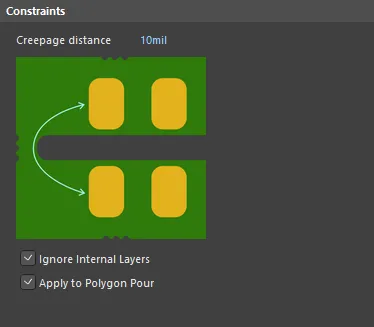
Default constraints for the Creepage distance rule
- Creepage distance – a rule violation is flagged when any point on the First Object is equal to or less than the distance from any point on the Second Object.
- Ignore Internal Layers – use this option to ensure the rule will only be applied to outer layers.
- Apply to Polygon Pour – use this option to apply the rule to scoped polygons.
Rule Application
Online DRC, Batch DRC, and during autorouting.
Notes
-
The Creepage Distance rule is not enabled for Online or Batch design rule checking by default. Enable Online/Batch checking in the Design Rule Checker dialog (Tools » Design Rule Check, Electrical category).
-
The display of rule violations may also need to be configured, Violation Details (localized violation information) and/or Violation Overlay (highlighting of the entire objects in violation) is enabled in the PCB Editor - DRC Violation Display page of the Preferences dialog.
-
The rule identifies the closest points on the targeted nets and checks the distance between them in the X, Y, and Z planes.
-
If a board slot has been created by placing a pad, make sure that the Plated option is disabled in the pad properties as the software assumes that the plated barrel is conductive and will reduce the creepage distance accordingly.
-
If a polygon pour and other objects are scoped by a Creepage Distance design rule with the Apply to Polygon Pour option enabled and a Clearance design rule, both rules are considered, and a larger value is applied when pouring the polygon. For example, if the Creepage Distance rule has a larger constraint value than the Clearance rule, this larger value will be applied.