3D Bodies are available for placement in the PCB and the PCB library editors in the following ways:
- In the PCB editor:
- In the PCB Library editor:
3D body objects can be placed with the display in 2D mode or 3D mode. When a 3D body is placed in 3D mode, object movement is restricted to the X, Y plane meaning that the cursor cannot be moved in the Z direction. Generally, it is easier to perform initial placement in 2D mode where objects can be aligned more easily.
To place a 3D Body object:
- After launching the placement command, the cursor will change to a crosshair and you will be in the default placement mode, placing an Extruded 3D Body object.
- Press Tab to pause placement and display the Inspector panel in 3D Body mode. The design space pause button overlay (
 ) will appear in the design space, indicating that you can access the fields of the Inspector panel.
) will appear in the design space, indicating that you can access the fields of the Inspector panel.
- In the Inspector panel, enter a name for the 3D Body in the Identifier field. This is optional; the Identifier can help when there are multiple 3D Bodies being placed and also can be used to target this 3D Body in a design rule, if required.
- Select the required Board Side; typically this is set to
Top. In the PCB library editor the footprint is built for the top side of the board; it can be flipped to the bottom during the PCB design process, if required.
- In the 3D Model Type region of the Inspector panel, click the Generic button.
- Click the Choose button to load the model file.
- In the standard Windows Open dialog that appears, browse to and locate the required model file and click Open. The cursor will change to a crosshair, with the selected 3D model floating on it.
- You will return to the Inspector panel, with the path and filename of the model displayed in the Path field.
- The default model color can be overridden if required. In the Display section of the panel, enable the Override Color checkbox then set the Color and the Opacity as required.
- Once editing in the panel is complete, click the pause button overlay to return to the design space.
- The model will be floating on the cursor; position it then click to place.
- It is quite likely that the generic model will need to be re-oriented. Use the commands in the Tools | 3D Body | 3D Body Placement menu or edit the X, Y & Z properties in the Inspector panel.
Graphical Editing
This method of editing allows you to select a placed 3D body object directly in the design space and change its size, shape, or location graphically.
Click on the 3D body then drag to reposition it. While dragging, the 3D body can be rotated or mirrored:
- Press the Spacebar to rotate the 3D body counterclockwise or Shift+Spacebar for clockwise rotation. The Rotation Step size is defined on the PCB Editor – General page of the System Preferences.
- Press the X or Y keys to mirror the 3D body along the X-axis or Y-axis.
An object that has its Locked property enabled cannot be selected or graphically edited. Double-click on the locked object directly then disable the Locked property to graphically edit the object.
To clear the selection of (or de-select) the object, use the Esc key.
Non-Graphical Editing
This method of editing uses the associated Inspector panel mode to modify the properties of a 3D Body object.
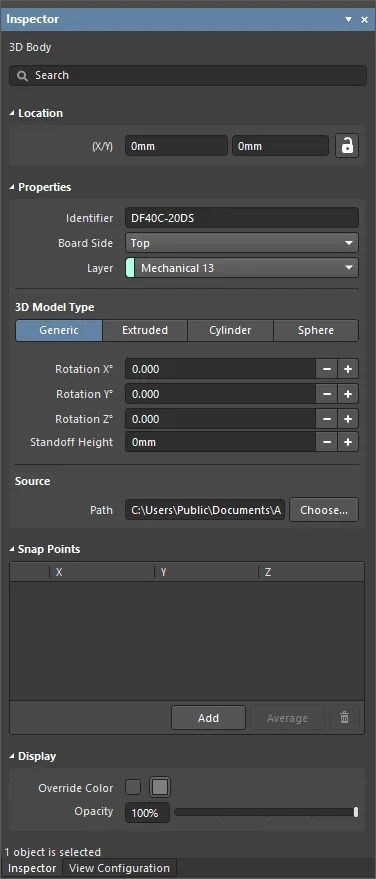
During placement, the 3D Body mode of the Inspector panel can be accessed by pressing the Tab key. Once the 3D Body is placed, all options appear.
After placement, the 3D Body mode of the Inspector panel can be accessed by:
- Double-clicking on the placed 3D Body object.
- Placing the cursor over the 3D Body object, right-clicking then choosing Properties from the context menu.
Editing Multiple objects
The inspector panel supports editing multiple objects, where the property settings that are identical in all currently selected objects may be modified. When multiples of the same object type are selected manually, an Inspector panel field entry that is not shown as an asterisk (*) may be edited for all selected objects.
Additional 3D Body Editing Features
Maintaining Component Clearances
Add Component Clearance design rules to check for collisions between components that include 3D body objects in the X, Y and Z planes. This allows you to check the clearance of components over another component. Multiple rules can be defined to handle different clearance requirements. Note that the Design Rule Check does not test if a 3D body object is passing through the board.
Configuring the Mechanical and Display Layers
3D Body objects are normally placed on a mechanical layer. If the 3D Body object is to represent a component, the 3D Body object should be added to the component footprint in the PCB library editor.
Any mechanical layer can be used to place 3D Body objects. Typically a layer is chosen and named and that layer is used for 3D Body objects only. Because PCB components can be mounted on either surface of the finished PCB, the software supports the pairing of mechanical layers. Working in exactly the same way as the paired top and bottom silkscreen layers, when a component is flipped from the top side to the bottom side, any object on a mechanical layer that is paired is automatically flipped onto the paired mechanical layer.
Layer pairing is not required for the rendering of the model in 3D; the software uses the Board Side property to determine which surface the object is on and in which direction to render the 3D Body. Layer pairs are important if you need to generate side-of-board assembly printouts that include components on one side of the board.
When mechanical layers have been paired in the
View Configuration panel, they become Component Layers and appear in the
Component Layers region of the
Layers list. Refer to the
View Configuration panel page for more information on pairing layers.
Reference Point and Snap Points
Reference and Snap Points provide a way of holding a 3D Body object during placement. If the Snap to Center option is enabled in the PCB Editor - General page of the System Preferences, the cursor will automatically snap to the nearest vertex/reference point /snap point when you click and hold to move the object.
Enable the
3D Body Reference Point / Custom Snap Points in the
System Colors region of the
View Configuration panel to display the Reference Point and Snap Points.
Defining Snap Points
Snap points are user-defined locations, which allow the object to be held at that location as it is moved in the design space. Snap points are typically assigned to an edge or corner of the object or a center location, for example, the center of a pin or mounting peg.
Snap points can be added by entering the X, Y & Z locations in the Snap Points region of the Inspector panel.