Embedded Board Array
Parent page: PCB Objects

A 2 x 2 board array that references a single PCB design
Summary
An embedded board array is a primitive design object. It allows you to create a PCB panel (representing the physical board from which the PCB is to be manufactured) as part of your PCB design project. This is also known as panelization. You can use this panel to hold an array of PCBs by using the embedded board array command. This command links the panel to the original PCB design files, stepping it out the specified number of times. You cannot edit the PCBs directly from the board array, only through their original files.
Multiple embedded board arrays can be placed and each can reference a different PCB file. By spacing out the boards in each array and then overlaying, rotating, and flipping the different embedded arrays, any panelization arrangement can be created. This can be used to reduce manufacturing costs by maximizing the number of PCBs per panel of PCB material.
Availability
Embedded Board Arrays are available for placement in the PCB Editor in one of the following ways:
- Choose Place » Embedded Board Array/Panelize from the main menus.
- Right-click in the workspace then choose Place » Embedded Board Array/Panelize from the context menu.
Placement
- After launching the command, the cursor will change to a crosshair and you will enter embedded board array placement mode. The location of the crosshair decides the lower-left corner of the board array.
- Position this corner of the array at the required location then click or press Enter to place.
- Continue placing further embedded board arrays or right-click or press Esc to exit placement mode.
Additional actions that can be performed during placement while the embedded board array is still floating on the cursor ;and before the embedded board array is anchored are:
- Press the Tab key to pause the placement and access the Embedded Board Array mode of the Properties panel from where its properties can be changed on-the-fly. Click the workspace pause button overlay (
 ) to resume placement.
) to resume placement. - Press the Spacebar to rotate the embedded board array. Rotation is counterclockwise and in 90° increments.
- Press the L key to flip the embedded board array to the other side of the board.
Graphical Editing
This method of editing allows you to select a placed embedded board array object directly in the workspace and change its location or orientation graphically.
When an embedded board array object is selected, it is distinguished by light gray background. The below images illustrate an un-referenced board array (first image) and a 2 x 2 array that references a single PCB design (second image).

An un-referenced board array

A 2 x 2 array that references a single PCB design
Click anywhere within the boundary of the array then drag to reposition it. The array is automatically 'grabbed' by its lower-left corner and the board array's location is used as the anchor point to the cursor. The embedded board array can be rotated or flipped while dragging in the following ways:
- Press the Spacebar to rotate the embedded board array. Rotation is counterclockwise and in 90° increments.
- Press the L key to flip the embedded board array to the other side of the board.
The following methods of non-graphical editing are available:
Editing Via the Properties Panel
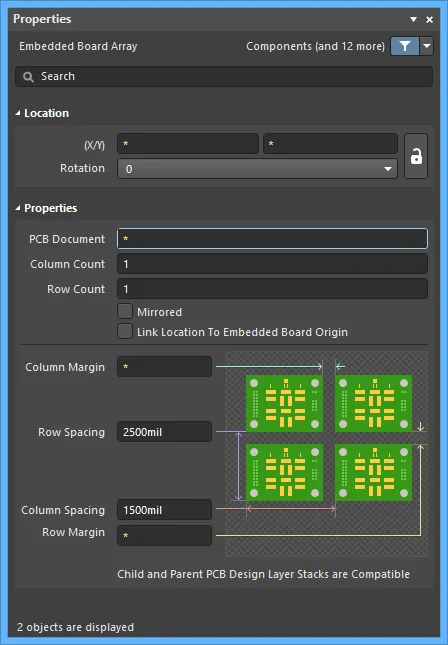
Properties page: Embedded Board Array Properties
This method of editing uses the associated Properties panel mode to modify the properties of an embedded board array object.

The Embedded Board Array mode of the Properties panel
During placement, the panel can be accessed by pressing the Tab key.
To access the properties of a placed embedded board array:
- Double-click anywhere on the embedded board array object.
- Right-click on the embedded board array then select Properties from the context menu.
- If the Properties panel is already active, click anywhere on the embedded board array object to select it.
Editing Multiple objects
The Properties panel supports editing multiple objects, where the property settings that are identical in all currently selected objects may be modified. When multiples of the same object type are selected manually, via the Find Similar Objects dialog or through a Filter or List panel, a Properties panel field entry that is not shown as an asterisk (*) may be edited for all selected objects.
Via the PCB List Panel
Panel page: PCB List
The PCB List panel allows you to display design objects from one or more documents in tabular format, enabling quick inspection and modification of object attributes. Used in conjunction with appropriate filtering, it enables the display of just those objects falling under the scope of the active filter – allowing you to target and edit multiple design objects with greater accuracy and efficiency.
Tips
- The embedded board array(s) used to create a representation of the manufacturing panel should be placed on a separate PCB document within the existing or alternate PCB project. This document should be considered the manufacturing 'hub' for other PCB documents that contain the actual designs.
- You can place additional objects to support panel manufacturing (for example, free pads as tooling holes), however, it is not advisable to place any other objects that would represent the actual physical design within the same document as the embedded board array(s).
- Since the embedded board array object references a PCB design file rather than containing a pasted copy of it, the source PCB design may be modified at any time. Once the reference file is saved, refresh the view of the panel document in order to bring the panel up-to-date.
- Gerber, NC Drill, ODB++, and printed output can be generated from a panel of embedded board arrays.
- When using the Design » Board Shape » Create Primitives From Board Shape command's Route Tool Outline option, you also can select the Include Cutouts option to simulate tool paths that contour board cutout edges.
- The software automatically attempts to resolve layer stack compatibility issues. The automatic layer stack synchronization process will attempt to:
- Ensure that all required child board layer stack ordered layers exist in the parent board (the PCB file containing the embedded board array).
- Modify the parent board layer stack in an attempt to achieve synchronization - a child board is never modified.
- Make only additive or layer type modifications to the parent board, layers are never removed.
