The PCB editor is a grid-based design environment - design objects are placed on what is referred to as the placement, or snap grid. Multiple snap grids can be defined, and these can be restricted to a specified area if required. Snap grids are prioritized, with the highest priority grid available at the current location, being applied automatically. Snap grids can also be restricted to Components or Non-Components.
Also, snap guides can be freely placed and provide a handy visual cue for object alignment.
This page describes how to configure snap grids and snap guides in your PCB document.
As well as snap grids and snap guides, the PCB editor includes a number of additional snap features, designed to help you accurately position and align design objects. Together, these features are referred to as the Unified Cursor-Snap System. Refer to the Working with the Cursor-Snap System page to learn more.
Imperial or Metric Grid?
Traditionally, the grid was selected to suit the component pin pitch and the routing technology that you planned to use for the board, i.e. how wide do the tracks need to be, and what clearance is needed between tracks. The basic idea is to have both the tracks and clearances as wide as possible to lower the fabrication costs and improve reliability. Of course, the selection of track/clearance is ultimately driven by what can be achieved on each design, which comes down to how tightly the components and routing must be packed to get the board placed and routed.
Over time, components and their pins have dramatically shrunk in size, as has the spacing of their pins. The component dimensions and the spacing of their pins have moved from being predominantly imperial with thru-hole pins to more-often being metric dimensions with surface mount pins. If you are starting a new board design, unless there is a strong reason, such as designing a replacement board to fit into an existing (imperial) product, you are better off working in metric. Why? Because the older, imperial components have big pins with lots of room between them. On the other hand, the small, surface mount devices are built using metric measurements – they are the ones that need a high level of accuracy to ensure that the fabricated/assembled/functional product works and is reliable. Also, the PCB editor can easily handle routing to off-grid pins, so working with imperial components on a metric board is not onerous.
User-Definable Grids
Any number of user-defined grids can be configured for the design space with all grid management performed from within the Grid Manager region of the Properties panel (accessed when there are no design objects currently selected in the design space). Use the controls available to define custom local grids by which to place design objects - especially components - with greater precision.
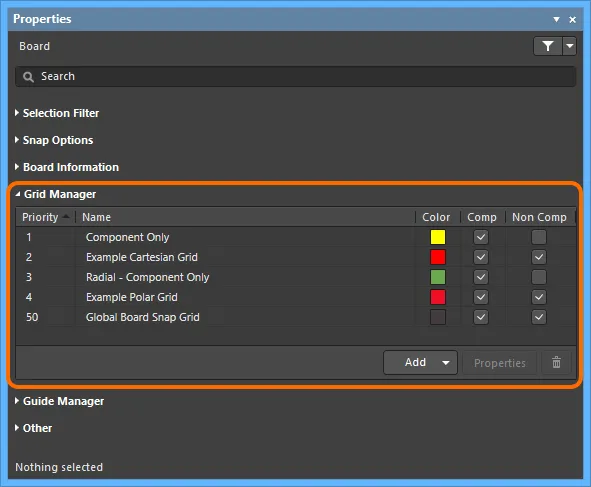
The Grid Manager region of the Properties panel is command central for defining and organizing the grids for use with your board.
Grid Types
The software supports the creation of two custom grid types: Cartesian (traditional vertical/horizontal grid) and Polar (circular grid).
-
Cartesian Grid - create a new grid of this type using the Add Cartesian Grid command (available from the  button, as described earlier). A new grid entry will appear in the list, initially with the default name New Cartesian Grid. To edit the grid, double-click on its entry or select its entry and click the
button, as described earlier). A new grid entry will appear in the list, initially with the default name New Cartesian Grid. To edit the grid, double-click on its entry or select its entry and click the  button. The Cartesian Grid Editor dialog will open presenting options with which to define the grid.
button. The Cartesian Grid Editor dialog will open presenting options with which to define the grid.
 Example Cartesian grid definition, using the Cartesian Grid Editor dialog, and resulting appearance in the design space.
Example Cartesian grid definition, using the Cartesian Grid Editor dialog, and resulting appearance in the design space.
Options and Controls of the Cartesian Grid Editor Dialog
For the default global snap grid, only the Settings, Steps and Display regions will be presented in the dialog.
Settings
-
Name – enter a meaningful name. For example, you might name the grid using a format that reflects its purpose (e.g., Grid for Component-Side Memory).
-
Unit – specifies the measurement units used for the grid either
Imperial or Metric.
-
Rotation – specifies whether the grid is to be rotated (about the specified origin point) and by how much.
Steps
-
Step X – the distance between grid lines in the X plane. Enter the required step size directly or select from a range of common sizes available in the associated drop-down.
-
Step Y – the distance between grid lines in the Y plane. Enter the required step size directly or select from a range of common sizes available in the associated drop-down.
By default, the two fields are linked as indicated by the continuous chain depicted on the button to the right of the fields –

. In this state, whatever you specify for the
Step X field will be copied and used for the
Step Y field. To break this link and enter step sizes individually, click the chain link. The link will display a broken chain –

– and the
Step Y field will be available for editing.
The following controls also are available that allow you to define the X and/or Y step sizes directly from within the PCB design space. In each case, you will be taken to the design space to specify two 'calculating' locations and the resulting step size will be calculated accordingly.
-
Set Step X in PCB View – the resulting size is taken as the hypotenuse of the triangle formed by the chosen points in the design space.
-
Set Step Y in PCB View – the resulting size is taken as the hypotenuse of the triangle formed by the chosen points in the design space.
-
Set Step X from Delta X – the resulting size is taken using just the difference in the X coordinate.
-
Set Step Y from Delta Y – the resulting size is taken using just the difference in the Y coordinate.
-
Set Both Steps from Delta – the resulting sizes are taken using just the differences in the X and Y coordinates.
Note that when Step Y is following Step X (with the chain "linked"), only the Set Step X in PCB View and Set Step X from Delta X controls are available.
Origin
-
Show Origin – enable to show an origin marker in the design space.
-
Origin X – specifies the X coordinate for the center point of the grid in the design space.
-
Origin Y – specifies the Y coordinate for the center point of the grid in the design space.
-
Set Origin in PCB View – click to be taken to the PCB design space, in which you can click to define the centerpoint for the grid's origin. The resulting coordinate values will be loaded into the Origin X and Origin Y fields.
Display
-
Fine – use the associated drop-down to define the markers used for the fine-level display of the grid in the design space, either Lines, Dots, or Do Not Draw. Choose Do Not Draw if you do not want to use the fine-level display grid. The step size used for the markers is that defined in the Steps region. Click on the associated color swatch to access the standard Choose Color dialog from where you can specify the color to be used for the fine-level display grid in the design space. You also can reset the color back to its default using the Reset to Default button.
-
Coarse – use the associated drop-down to define the markers used for the coarse-level display of the grid in the design space, either Lines, Dots, or Do Not Draw. Choose Do Not Draw if you do not want to use the coarse-level display grid. The coarse-level display grid is the fine-level display grid with an increased step size, in accordance with the entry selected in the Multiplier field. Click on the associated color swatch to access the standard Choose Color dialog from where you can specify the color to be used for the coarse-level display grid in the design space. You are free to choose a completely different color to that used for the fine-level display grid. You also can quickly lighten or darken the shade of the color currently used for the fine-level display grid by clicking the Lighter or Darker buttons.
The default display colors that are assigned to the
Fine and
Coarse display grids when the
Reset to Default button is clicked are defined in the
System Colors region of the
View Configuration panel (shortcut
L).
-
Multiplier – use this field to specify the required multiple of the grid's step size, either
2x Grid Step, 5x Grid Step, or 10x Grid Step.
Extents
-
Width – use this field to define the width of one quadrant of the grid.
-
Height – use this field to define the height of one quadrant of the grid.
By default, the two fields are linked, as indicated by the continuous chain depicted on the button to the right of the fields –

. In this state, whatever you specify for the
Width field will be copied and used for the
Height field. To break this link and enter values individually, click this chain link. The button will now depict a broken chain –

– and the
Height field will be available for editing.
Controls are also available that allow you to define the width and/or height directly from within the PCB design space. In each case, you will be taken to the design space to specify two 'calculating' locations, and the resulting width and/or height will be calculated accordingly.
-
Set Width in PCB View – the resulting width is taken using just the difference in the X coordinate between the chosen points in the design space.
-
Set Height in PCB View – the resulting height is taken using just the difference in the Y coordinate between the chosen points in the design space.
-
Set Width and Height in PCB View – the resulting width and height are taken using just the differences in the X and Y coordinates.
Note that when Height is following Width (chain is linked), only the Set Width in PCB View control is available.
Quadrants
Use this region to specify which quadrants the grid is to occupy. The grid area is the same for all enabled quadrants as defined by the setting for Width and Height in the Extents region of the dialog.
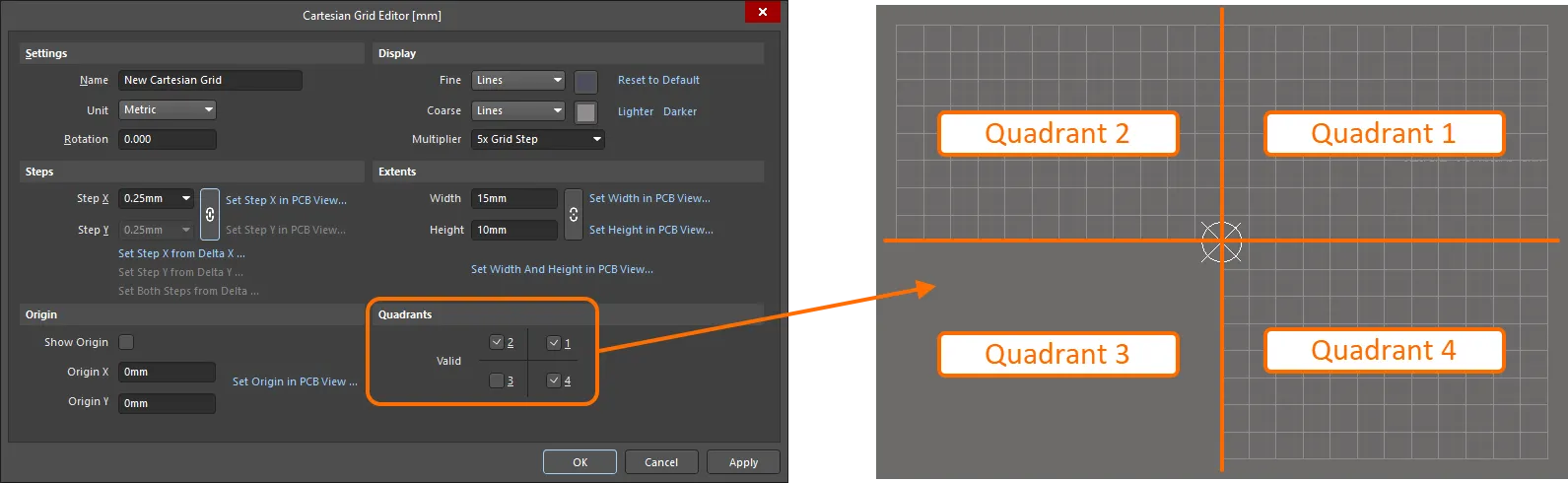
Example of using the Quadrants region options. Note that only 1, 2, and 4 quadrants are enabled for use, and the resulted grid occupies only these quadrants relative to the grid origin.
-
Polar Grid - create a new grid of this type using the Add Polar Grid command (available from the  button, as described earlier). A new grid entry will appear in the list, initially with the default name New Polar Grid. To edit the grid, double-click on its entry or select its entry then click the
button, as described earlier). A new grid entry will appear in the list, initially with the default name New Polar Grid. To edit the grid, double-click on its entry or select its entry then click the  button. The Polar Grid Editor dialog will open presenting options with which to define the grid.
button. The Polar Grid Editor dialog will open presenting options with which to define the grid.
 Example Polar grid definition using the Polar Grid Editor dialog and resulting appearance in the design space.
Example Polar grid definition using the Polar Grid Editor dialog and resulting appearance in the design space.
Options and Controls of the Polar Grid Editor Dialog
Settings
-
Name - use this field to give the polar grid a meaningful name. For example, you might name the grid using a format that reflects its purpose (e.g.,
Grid for Component-Side Memory).
-
Unit - use this field to specify the measurement units used for the grid: Imperial or Metric.
Steps
-
Angular Step - use this field to define the distance, in degrees, between the angular grid lines. This value is used to equally space the angular grid lines over the defined angular range.
-
Radial Step - use this field to define the distance between the radial grid lines. Type the required step size directly or select from a range of common sizes available in the associated drop-down list.
-
Set Radial Step in PCB View - click to define the radial step directly from within the PCB design space. You will be taken to the design space to specify two 'calculating' locations – the resulting step size is taken as the hypotenuse of the triangle formed by the chosen points in the design space.
Origin
-
Origin X - use this field to specify the X coordinate for the center point of the grid in the design space.
-
Origin Y - use this field to specify the Y coordinate for the center point of the grid in the design space.
-
Set Origin in PCB View - click this control to be taken to the PCB design space in which you can click to define the centerpoint for the grid's origin. The resulting coordinate values will be loaded into the Origin X and Origin Y fields.
Display
-
Fine - use the associated drop-down to define the markers used for the fine-level display of the grid in the design space, either
Lines, Dots, or Do Not Draw. The step size used for the markers is that defined in the Steps region. Click on the associated color swatch to access the standard Choose Color dialog in which you can specify the color to be used for the fine-level display grid in the design space. If you do not want to use the coarse-level display grid, choose the Do Not Draw option. You also can reset the color back to its default using the Reset to Default link.
-
Coarse - use the associated drop-down to define the markers used for the coarse-level display of the grid in the design space, either
Lines, Dots, or Do Not Draw. The coarse-level display grid is the fine-level display grid with an increased step size in accordance with the entry selected in the Multiplier field. If you do not want to use the coarse-level display grid, choose the Do Not Draw option. Click on the associated color swatch to access the standard Choose Color dialog in which you can specify the color to be used for the coarse-level display grid in the design space. You are free to choose a completely different color to that used for the fine-level display grid. Alternatively, you can quickly employ a lighter or darker shade of the color currently used for the coarse-level display grid using the available Lighter or Darker links. You also can reset the color back to its default using the Reset to Default link.
-
Multiplier - use this field to specify the required multiple of the grid's step size, either
2x Grid Step, 5x Grid Step, or 10x Grid Step.
The default display colors that are assigned to
Fine and
Coarse display grids when the
Reset to Default link is clicked are defined in the
General Settings region on the
View Options tab of the
View Configuration panel.
Angular Range
-
Start Angle - use this field to configure at which angle the polar grid begins.
-
End Angle - use this field to configure at which angle the polar grid ends.
If the start angle and end angle are set to the same number, the dialog will automatically update to Start Angle 00.000 and End Angle 360.000. The polar grid will display as a full 360°.
Radial Range
-
Min - use this field to set the minimum diameter of the polar grid.
-
Max - use this field to set the maximum diameter of the polar grid.
The diameters of the Radial Range are measured from the origin point out and set the radial extents of the grid.
Quickly access the relevant editor for a defined grid in the design space by hovering the cursor over an area of the board using that grid (do not click in the design space prior to launching the command) and either pressing the
Ctrl+G keyboard shortcut or using the
G keyboard shortcut, then choosing the
Grid Properties entry on the subsequent pop-up menu.
Default Snap Grid
A default snap grid is defined for the board, named Global Board Snap Grid. This is the grid that is used for object placement and movement in any area of the board not covered by a dedicated local grid. Note that the default grid always applies to the entire design space even though it is only displayed over the board shape.
 Global Board Snap Grid - used in any area of the board where a custom local grid has not been defined.
Global Board Snap Grid - used in any area of the board where a custom local grid has not been defined.
The default grid is a Cartesian-type grid. The step size and/or display for the grid can be modified, but the grid cannot be renamed, disabled, or deleted.
Changing Default Snap Grid Sizing, Measurement Units, and Overriding a Snap Grid
Within the design space, the G keyboard shortcut gives you access to a menu of commands for quickly setting the X (horizontal) and/or Y (vertical) step values for the default Global Board Snap Grid. These commands only affect the default snap grid for the board and not any custom grids (Cartesian and polar) that you may have defined. Commands are available to quickly switch to another predefined step sizing or to access the Snap Grid (1..1000) dialog (shortcut: Ctrl+Shift+G), with which you can define a specific, custom sizing.
The Snap Grid (1..1000) dialog
Application of the predefined/custom value depends on whether you are setting both X and Y step values simultaneously or X or Y step values individually:
-
Setting X and Y step values simultaneously - if the Step X and Step Y properties of the Global Board Snap Grid were previously unlinked, this command will link the two, with both set to the same predefined/custom value.
-
Setting X or Y step values individually - if the Step X and Step Y properties of the Global Board Snap Grid were previously linked, this type of command will unlink the two, with only the chosen (X or Y) step value set to the predefined/custom value. The other step value will remain at its previous setting.
If entering a snap grid setting without specifying units, the entry will be in the default measurement units selected for the design as determined by the Units setting in the Other region in the Board mode of the Properties panel. Specifying units when entering the value (mm or mil) in this dialog will change the default measurement units for the document if not currently the default.
The current snap grid setting for the grid (default or custom local) currently under the cursor is always displayed on the Status Bar along with the cursor location relative to the Current Origin. If the grid was set globally (for both Step X and Step Y), then a single entry for the grid value will be displayed. If the grid was set for Step X or Step Y individually, the individual grid steps will be displayed.
The current origin is user-definable and can be located anywhere in the design space; the Absolute Origin is the bottom-left (0,0) of the design space (100X x 100Y inch, which is the maximum).
 The Status Bar always displays the current snap grid and the cursor location relative to the Current Origin.
The Status Bar always displays the current snap grid and the cursor location relative to the Current Origin.
The Status Bar also reflects the current state of object Hotspot Snapping. Object hotspot snapping provides an aid to routing electrical objects, especially those which may not fall on the default Global Board Snap Grid, or a defined custom grid. It gives you a distance, or range, in which the cursor can be away from an object but still snap to the object's hotspot (e.g., the center of a pad). Object hotspot snapping overrides a snap grid, allowing you to easily connect to an off-grid object. Use the Shift+E keyboard shortcut to cycle through the three modes (Off, Current Layer, All Layers). For more information, see Object Snapping.
To toggle the markers used for the fine-level display of the default Global Board Snap Grid between lines and dots when in the design space, choose the View » Grids » Toggle Visible Grid Kind command from the main menus.
Defining the Purpose of a Grid
A local grid can be used in a variety of situations:
-
In the placement of non-component objects only.
-
In the placement of component objects only.
-
In the placement of both non-component and component objects.
Definition of how a grid can be used (its purpose or application) is performed using the Comp and Non Comp options associated with that grid's entry in the Grid Manager region of the Properties panel, in accordance with the following table:
| |
NON COMP = Cleared |
NON COMP = Enabled |
| COMP = Cleared |
Grid is not visible but still applied in accordance with the current snap behavior settings |
Grid visible and applied for all non-component object actions |
| COMP = Enabled |
Grid is only visible and applied during component actions |
Grid is visible and applied for actions on all kinds of objects |
 Use the Comp and Non Comp options to determine local grid application.
Use the Comp and Non Comp options to determine local grid application.
-
When specifying a component-only grid (Non Comp option disabled, Comp option enabled), the grid will only display when performing a component-based action, such as moving a component.
-
The visibility of the default snap grid does not determine if it is being applied, that is controlled by the current snap grid behavior settings.
Example Grid Usage
The following animation illustrates an example of using a local Polar Grid for component placement in the PCB Editor. The grid has been defined for use with components only, and therefore, only appears when a component starts to be moved. This example also illustrates a great feature of polar grids - automatic placement rotation. As you move a component over a defined grid of this type, it will automatically rotate to the origin of the grid as you move it around the grid. Use this feature in combination with standard object rotation - Spacebar (counter-clockwise), Shift+Spacebar (clockwise) - to align your components exactly as you need them.
 An example of component placement on a component-only local Polar Grid.
An example of component placement on a component-only local Polar Grid.
Defining the Grid Display
For any custom grid you define, as well as the Global Board Snap Grid, options are provided to control how the grid is presented visually in the design space. Two levels can be defined:
-
Fine - the fine-level display grid is for when you are more zoomed-in. The grid markers for this level of grid display follow directly the defined step sizes for the grid.
-
Coarse - the optional coarse-level display grid comes into play as you zoom out. The grid markers for this level of grid display are based on a specified multiple of the defined step sizes.
 Example Cartesian grid with fine- and coarse-level display grids presented in the design space. Left: Fine-level displayed using dots, coarse-level using Lines. Right: Both fine- and coarse-level grids displayed using Lines.
Example Cartesian grid with fine- and coarse-level display grids presented in the design space. Left: Fine-level displayed using dots, coarse-level using Lines. Right: Both fine- and coarse-level grids displayed using Lines.
Individual grid display coloring is defined when editing a grid in the relevant grid editor (
Cartesian Grid Editor dialog or
Polar Grid Editor dialog). Alternatively, a single nominated color can quickly be assigned for the Fine and Coarse display grids in the
Grid Manager region of the
Properties panel. To do this, click the color swatch in the grid's associated
Color field then choose the required color from the subsequent color palette that appears.
Fine and Coarse display grid colors can be reset to a specified default color by clicking the
Reset to Default link in a grid editor. Default coloring is defined in the
General Settings region on the
View Options tab of the
View Configuration panel. Click the color swatch to the right of the
Show Grid option then choose the required color from the color palette that appears. Note that this single default color will be used for both Fine and Coarse display grids. Note also, that changing the color here will affect only the default
Global Board Snap Grid. Existing custom grids will retain the display colors set for them - only reverting to this new color if the
Reset to Default link is used.
Nesting and Grid Priority
The local grids you define in the Grid Manager region of the Properties panel can be freely stacked within the board area. By specifying origin coordinates accordingly, grids can be overlapped, creating a nested hierarchy of grids with which to fine-tune the placement of design objects as you layout your board.
Grid contention - which grid in an overlapping stackup of grids should a design object snap to - is resolved using a priority system. Each local placement grid you create and define is given a numbered priority. By default, each new grid is given the highest priority of 1, with all existing grids moved down in priority accordingly.
The Global Board Snap Grid is an exception. As it is the default grid that is used in all areas of the board that are not 'covered' by defined custom grids, it is given the priority setting of 50 - a low enough priority setting to ensure that it has the lowest 'snapping priority' of all defined grids.
In the design space, priority is distinguished by drawing order. The highest priority grid (priority 1) will be drawn in front of all other grids, then the grid with priority level 2, and so on, down to the default Global Board Snap Grid, which is drawn behind all other custom grids.
 An example of three nested Polar grids. The Yellow Polar Grid has the highest priority and appears on top. The Red Polar Grid is the next priority, appearing behind the yellow grid but in front of the aqua grid. The default grid appears behind all of these grids, as all custom grids take precedence over it in the priority stakes.
An example of three nested Polar grids. The Yellow Polar Grid has the highest priority and appears on top. The Red Polar Grid is the next priority, appearing behind the yellow grid but in front of the aqua grid. The default grid appears behind all of these grids, as all custom grids take precedence over it in the priority stakes.
The priority of the Global Board Snap Grid cannot be changed; it is fixed to always have a priority of 50.
Disabling a Grid
There may be occasions where a grid is not needed while placing or moving a particular design object. Rather than deleting the grid (since it may be needed again later in the same or different area of the board), it can be 'hidden' in the design space. This can be achieved by disabling the grid's associated Comp and Non Comp attributes in the Grid Manager region of the Properties panel.
 Disable a local grid to effectively hide it, therefore preventing objects from snapping to it. Using the nested grids example, the Red Polar grid has been disabled. As the grid has not been deleted, you can re-enable and use it again when needed without having to redefine it!
Disable a local grid to effectively hide it, therefore preventing objects from snapping to it. Using the nested grids example, the Red Polar grid has been disabled. As the grid has not been deleted, you can re-enable and use it again when needed without having to redefine it!
The default
Global Board Snap Grid is permanently enabled, as this is the default grid that is used when no local grid has been defined for an area of the board. However, it and all defined grids can be hidden by disabling the
Show Grid option in the
General Settings region on the
View Options tab of the
View Configuration panel.
Deleting a Grid
Custom grids can be deleted by selecting their corresponding entry in the Grid Manager region of the Properties panel then clicking the  button. You will be asked to confirm the deletion. Click Yes to do so.
button. You will be asked to confirm the deletion. Click Yes to do so.
Remember that the default Global Board Snap Grid cannot be deleted.
Snap Guides
Snap Guides are special objects that are manually placed specifically for the purpose of driving the cursor-snap on a certain axis or point - assisting in object/component placement. They can also serve as a visual indicator for general layout or alignment purposes. The following types of snap guides are supported:
-
Linear Guide - a line-style guide that can be horizontal, vertical or +/- 45 Degrees.
-
Point Guide - a point-style guide offering finer control over object placement. It is simply a hotspot that is manually marked within the confines of a defined grid.
Any number of snap guides can be defined for the design space with controls for placement and management available from the Guide Manager region of the Properties panel (accessed when there are no design objects currently selected in the design space). While controls are available for adding new snap guides from within this region (from the  button), it is far easier to visually add them (from the
button), it is far easier to visually add them (from the  button) directly in the design space then fine-tune them as required.
button) directly in the design space then fine-tune them as required.
Snap Guides can also be placed using commands available from the Place » Work Guides sub-menu.
Snap Guides behave in the same manner as the snap grid. The cursor will snap to a guide as it passes when an object is being moved.
 The Guide Manager region of the Properties panel is command central for managing visual placement guides for use in the design space. These are examples of the various Snap Guides available to assist object placement.
The Guide Manager region of the Properties panel is command central for managing visual placement guides for use in the design space. These are examples of the various Snap Guides available to assist object placement.
During an interactive process such as placing or moving, the cursor will snap to a placed Linear Guide at the point where that guide intersects a defined grid. Using a Linear Guide, objects can quickly be aligned by dragging them until they 'snap' against the guideline. For a Point Guide, the hotspot for the object being moved will 'snap' to the guide when it passes into close proximity with it.
It can be easier to visually locate a Point Guide when the grid display is set to Dots.
Disabling a Guide
There may be occasions where a snap guide is not needed while placing or moving a particular design object. Rather than deleting the guide (since it may be needed again later in the same or different area of the board), it can be 'hidden' in the design space. This can be achieved by disabling the guide's associated Enabled attribute in the Guide Manager region of the Properties panel.
 Disable a snap guide to effectively hide it, therefore preventing objects from snapping to it. In this image, the +45 and -45 guides have been disabled. As the guides have not been deleted, you can re-enable and use them again when needed without having to redefine them!
Disable a snap guide to effectively hide it, therefore preventing objects from snapping to it. In this image, the +45 and -45 guides have been disabled. As the guides have not been deleted, you can re-enable and use them again when needed without having to redefine them!
Deleting a Guide
To delete a snap guide, select its entry in the Guide Manager region of the Properties panel then click the  button. You will be asked to confirm the deletion. Click Yes to do so.
button. You will be asked to confirm the deletion. Click Yes to do so.